Wednesday, January 3, 2018
Deep Dive : firewalld in CentOS 8 / CentOS 7 / RedHat 7 / RedHat 8
Introduction
firewalld (firewall demaon) is firewall management tool to manage firewall. it is frontend controller for iptables. it is used to implement persistence traffic rules.
It is available in Command Line as well as Graphical Interface.
Note : It is not replacement of iptables, while it is wrapper of iptables, and provide flexibility to manage iptables.
firewalld architecture
Installing and Managing firewalld
By default firewalld included with CentOS 8 / Redhat 8 / CentOS 7 / RedHat 7,but if it is not installed then we can installed it by following yum / dnf command.
$ sudo yum -y install firewalld
firewalld have two tools
1. Graphical -> firewall-config
2. Command Line -> firewall-cmd
Difference between ip*tables and firewalld
iptables stores configuration in /etc/sysconfig/iptables and /etc/sysconfig/ip6tables while firewalld store it in various xml files in /usr/lib/firewalld/ and /etc/firewalld/
with iptables service, every single change means flusing all the old rule and reading all new rule from /etc/sysconfig/iptables,while with firewalld there is no recreating of all the rules.
To Start the firewalld
$ sudo systemctl start firewalld
To enable firewalld - enable firewalld at boot time
$ sudo systemctl enable firewalld
To Stop and disable firewalld
$ sudo systemctl stop firewalld $ sudo systemctl disable firewalld
To Check firewalld status
$ firewall-cmd --state running
To view status of firewall daemon
$ systemctl status firewalld ● firewalld.service - firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Tue 2018-01-02 10:27:26 IST; 1 day 2h ago Docs: man:firewalld(1) Main PID: 1081 (firewalld) CGroup: /system.slice/firewalld.service └─1081 /usr/bin/python -Es /usr/sbin/firewalld --nofork --nopid Jan 02 10:27:26 dev.driveo.in systemd[1]: Starting firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon... Jan 02 10:27:26 dev.driveo.in systemd[1]: Started firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon. Hint: Some lines were ellipsized, use -l to show in full.
$ firewall-cmd --reload
Configuration of firewalld
firewalld is configured with xml files.
configuration files are located in two directories :
- /usr/lib/firewalld - hold default configuration , like default zones and common services. Avoid updating them because these files are updated each time when firewalld package update
- /etc/firewalld - hold system configuration file. these file overwritten default configuration.
Configuration set
firewalld has two configuration sets : runtime and permanent.
runtime - configurations are volatile in nature at reboot it changed. runtime is default.
permanent - it persistence configuration not change after reboot.
Add rule to permanent or runtime
1 Permanent
$ sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service=http --permanent
2. Runtime
$ sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service=http
reload firewalld
reload command drop all runtime configuration
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Firewall zones
zones are pre-constructed rule sets for various trust level . After enabling firewalld first time public is default zone.
zones can be applied different network interface cards.
- drop
- Any incoming network packets are dropped; there is no reply. Only outgoing network connections are possible.
block- Any incoming network connections are rejected with an icmp-host-prohibited message for
IPv4and icmp6-adm-prohibited forIPv6. Only network connections initiated from within the system are possible. public- For use in public areas. You do not trust the other computers on the network to not harm your computer. Only selected incoming connections are accepted.
external- For use on external networks with masquerading enabled, especially for routers. You do not trust the other computers on the network to not harm your computer. Only selected incoming connections are accepted.
dmz- For computers in your demilitarized zone that are publicly-accessible with limited access to your internal network. Only selected incoming connections are accepted.
work- For use in work areas. You mostly trust the other computers on networks to not harm your computer. Only selected incoming connections are accepted.
home- For use in home areas. You mostly trust the other computers on networks to not harm your computer. Only selected incoming connections are accepted.
internal- For use on internal networks. You mostly trust the other computers on the networks to not harm your computer. Only selected incoming connections are accepted.
trusted- All network connections are accepted.
- The zone names and settings are proposals and can be changed according to the needs. A built-in zone cannot be removed, but it is possible to revert the zone configuration back to the initial defaults by loading the zone defaults either in the permanent configuration of firewall-config or
firewall-cmd
To view default zones
sudo fiewall-cmd --get-default-zone
To set default zones
sudo firewall-cmd --set-default-zone=dmz
To view zones used by network interface card
sudo firewall-cmd --get-active-zone
To get all the configuration for a specific zone
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-all
To get all the configuration for all zones
sudo firewall-cmd --list-all-zones
Predefined Services
A service can be a list of local ports, protocols, source ports, and destinations as well as a list of firewall helper modules automatically loaded if a service is enabled.
To list all services available on the system, enter the following command:
~]$
firewall-cmd --get-servicesTo get the settings of a service, use the following command:
~]$
firewall-cmd --info-service=service-name we can also view available list of services by accessing /usr/lib/firewalld/services directory.
Note : /usr/lib/firewalld/services/ directory must not be edited. only the file inside /etc/firewalld/services should be edited.
Services can be add or edited by firewall-cmd , firewall-offline-cmd, firewall-config tools. alternatively we can edit /etc/firewalld/services/ xml files.
enter the following command to add a new and empty service:
~]$ firewall-cmd --permanent --new-service=service-name
To add a new service using a local file, use the following command:
~]$ firewall-cmd --permanent --new-service-from-file=service-name.xml As soon as service settings are changed, an updated copy of the service is placed into /etc/firewalld/services/. As root, you can enter the following command to copy a service manually ~]# cp /usr/lib/firewalld/services/service-name.xml /etc/firewalld/services/service-name.xml firewalld loads files from /usr/lib/firewalld/services in the first place. If files are placed in /etc/firewalld/services and they are valid, then these will override the matching files from /usr/lib/firewalld/services. The overriden files in /usr/lib/firewalld/services will be used as soon as the matching files in /etc/firewalld/services have been removed or if firewalld has been asked to load the defaults of the services. This applies to the permanent environment only. A reload is needed to get these fallbacks also in the runtime environment.Configuring firewalld
firewall service can be configured by firewall-cmd ,firewall-config or firewall-offline-cmd or by editing xml configuration files.
1. firewall-config - it is graphical tool.
to start graphical interface enter following command.
$ firewall-config
Firewall configuration window open, note this command can be run as normal user but administrator password asked for validation.
Location:
Delhi, India
Tuesday, January 2, 2018
Configure EC2 CentOS 7 instance for running JAVA Applications, Also Connect Tomcat and Apace with mod_jk
Prerequisites
Knowledge of creating EC2 instance.
Configure CentOS 7
STEP 1 :
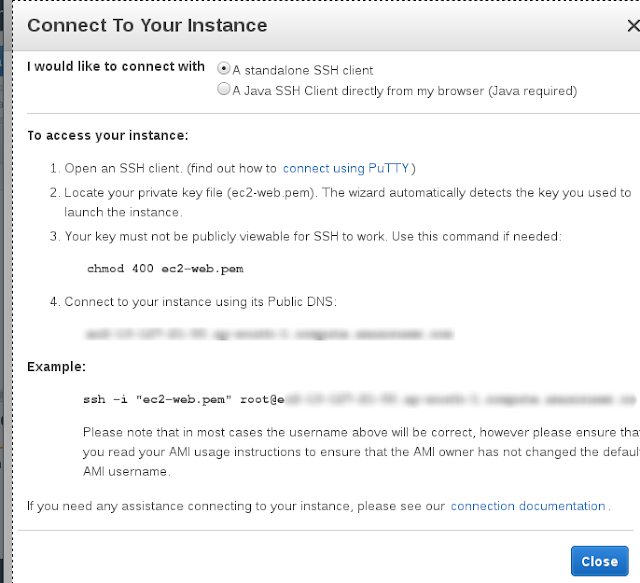
Launch terminal of CentOS EC2 instance by using private key file.
Note : Private key file publicly not visible. set it
chmod 400 <privatekeyfile>
connect terminal by using
ssh -i <path to privatekeyfile/privatekeyfile.pem> centos@<elasticIP>
or
ssh -i <path to privatekeyfile/privatekeyfile.pem> centos@<public dns>
Note 2 : You can get this information By Clicking on connect button of ec2 instance web console
Note 3 :
Monday, January 1, 2018
How to run command after closing terminal
Sometime we required to run some services, if we disconnect terminal they run continually.
This is very simple use & at the end of command.
$ java - jar product.jar &
this will run product.jar after disconnecting terminal
Write Trigger in Microsoft SQL SERVER
Recently i got a project where client use Shoper as POS and HO for managing its sales and purchase. I need to fetch Order along with customer details.
Shoper database in sql server, but it has no relationship among table. My database is one to many relationship between customer and order.
So I write a trigger , When new record inserted in shopper table i fetch this records and insert it into my database after selecting all the desire attribute.
create Trigger customerAudit on stktrndtls
After Insert
AS
Declare @TrnCtrlNo varchar(10);
declare @DocNoPrefix varchar(10);
declare @DocEntNetValue varchar(10);
declare @DocDt datetime;
declare @DocEntTotDisc varchar(10);
declare @StockNo varchar(32);
declare @OrdDocNo int;
declare @DocNo varchar(10);
declare @DiscRate varchar(10);--money
declare @VACompCode varchar(10);
declare @ItemMRPBillTm varchar(10);--money
declare @PhyQtyOut varchar(3);
declare @StkUpdtRate varchar(10);
declare @StkUpdtValueOut Varchar(10);
declare @Class1Cd varchar(16);
declare @Class2Cd varchar(16);
declare @SubClass1Cd varchar(16);
declare @SubClass2Cd varchar(16);
declare @Retail_Price varchar(10);--money
declare @ItemDesc varchar(60);
declare @PartyId varchar(16);
declare @TotDocValue varchar(20);
declare @TotDocDisc varchar(20);
declare @Code varchar(16);
declare @Nm varchar(30);
declare @check varchar(11);
--declare @mddate datetime;
--declare @epoc number(20);
BEGIN
select @TrnCtrlNo=i.TrnCtrlNo from inserted i;
select @DocNoPrefix=i.DocNoPrefix from inserted i;
print @TrnCtrlNo;
select @DocEntNetValue=i.
select @DocDt=i.DocDt from inserted i;
select @DocEntTotDisc=i.DocEntTotDisc from inserted i;
select @StockNo=i.StockNo from inserted i;
select @OrdDocNo=i.OrdDocNo from inserted i;
select @DocNo=i.DocNo from inserted i;
select @DiscRate=i.DiscRate from inserted i;
select @VACompCode=i.VACompCode from inserted i;
select @ItemMRPBillTm=i.ItemMRPBillTm from inserted i;
select @PhyQtyOut=i.PhyQtyOut from inserted i;
SELECT @StkUpdtRate=i.StkUpdtRate from inserted i;
select @StkUpdtValueOut=i.
select @Class1Cd=m.Class1Cd from ItemMaster m where m.StockNo=@StockNo;
select @Class2Cd=m.Class2Cd from ItemMaster m where m.StockNo=@StockNo;
select @SubClass1Cd=m.SubClass1Cd from ItemMaster m where m.StockNo=@StockNo;
select @SubClass2Cd=m.SubClass2Cd from ItemMaster m where m.StockNo=@StockNo;
select @Retail_Price=m.Retail_Price from ItemMaster m where m.StockNo=@StockNo;
select @ItemDesc=m.ItemDesc from ItemMaster m where m.StockNo=@StockNo;
select @PartyId=h.PartyId from stktrnhdr h where h.DocNo=@DocNo;
select @TotDocValue=h.TotDocValue from stktrnhdr h where h.DocNo=@DocNo;
select @TotDocDisc=h.TotDocDisc from stktrnhdr h where h.DocNo=@DocNo;
select @Nm=c.Nm from Customers c where c.Code=@PartyId;
print @NM;
update stktrndtls set unread='N' from inserted;
select @check=o.mobile from fbCustomer o where o.mobile=@PartyId;
if @check is null
--amount varchar(12), bill_number varchar(12),order_date varchar(12),
--order_time varchar(12),discount varchar(10),channel varchar(10),store_id varchar(10)
insert into fbcustomer(customerName,
values(@Nm,@PartyId,@
else
update fbCustomer set customerName=@Nm,mobile=@
/*
mobile varchar(10) not null,
[gTotal] [varchar](50) NULL,
[billNumber] [varchar](50) NULL,
[orderDate] [varchar](50) NULL,
[orderTime] [varchar](50) NULL,
[discount] [varchar](50) NULL,
[catID] [varchar](50) NULL,
[catName] [varchar](50) NULL,
[subCatID] [varchar](50) NULL,
[subCatName] [varchar](50) NULL,
[prodID] [varchar](50) NULL,
[prodName] [varchar](50) NULL,
[qty] [varchar](50) NULL,
[prodPrice] [varchar](50) NULL,
[storeID] [varchar](50) NULL,
[storeName] [varchar](50) NULL,*/
insert into fbOrders(mobile,gTotal,
prodName,qty,prodPrice,
values(@PartyId,@
@Class2Cd,@SubClass1Cd,@
/*insert into xtcust(customerName,mobile,
catName,subCatID,subCatName,
values(@Nm,@PartyId,@
@Class2Cd,@SubClass1Cd,@
end ;
In this I convert current datetime to epoch format
select datediff(ss,'1970-
following query convert 20/11/2017 23:12:02.000 into EPOCH format
select DATEDIFF(s, '1970-01-01 00:00:00', '2017-11-20 23:12:02.000') as EpochTimeStamp
Converting a timestamp to epoch unix formatRETURN
(CAST(ts AS DATE) - DATE '1970-01-01') * 86400
+ (EXTRACT(HOUR FROM ts) * 3600)
+ (EXTRACT(MINUTE FROM ts) * 60)
+ (EXTRACT(SECOND FROM ts))
How to install AWS CLI in CentOS (Linux) and setup programming environment
Introduction
AWS Command Line Interface(CLI) is a unified tool to manage your AWS Services. With the Help of this tool you can manage , configure and control multiple services.
AWS CLI Version
Currently two version of AWS CLI -
AWS CLI Version 1 - It's Older version , have less feature than version 2.
AWS CLI Version 2 - It's Latest version and supported all latest feature of AWS.
Step by Step Installing AWS CLI at Linux
Installing AWS CLI Version 1
Step 1 : First we update current system, to ensure all packages have latest version.$ sudo yum -y updateStep 2 : You can install AWS CLI and its dependency by using pip. Check pip and python installation status.
If python3 is installed then it is recommended that use pip3 also.
Check python installation status
$ python --versionor
$ python3 --versionCheck pip installation status
$ pip --versionor
$ pip3 --versionIf PIP already installed then ignore Step 3
Step 3 : Install pip - If you have don't have python or python3 on your Linux box then follow this step by step guide. Now download pip script provided by python packaging authority.
- Download pip script by using curl with -O option.
$ curl -O https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py
- For python
$ python get-pip.py --user
- For python3
$ python3 get-pip.py --user
- Now test pip install correctly
$ pip --version pip 20.0.2 from /home/yogesh/.local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/pip (python 3.6)or
$ pip3 --version pip 20.0.2 from /home/yogesh/.local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/pip (python 3.6)
Step 4 : Install AWS CLI
Use pip or pip3 to install aws cli.
$ pip install --upgrade awscli --useror
pip3 install --upgrade awscli --userwhen you use --user switch, it install locally
Step 5 : Verify AWS CLI installation
aws --version
Installing AWS CLI Version 2
AWS CLI V2 is complete software package it not required any other package. you no need to install python.
Step 1 : Download file using curl, use -o(smallcase letter o) option to rename downloaded file from awscli-exe-linux-x86_64.zip to awscliv2.zip
Step 2 : Unzip awscliv2.zip using unzip command
optional switch
--install-dir - specific location other than default location which under current user.
--bin-dir - specific bin directory
--update - if you want update from version 1 to version 2
Step 1 : Find bin directory of AWS CLI Version 1 result give --bin-dir parameter valuePrerequisite
Required unzip package to extract the downloaded file.Step 1 : Download file using curl, use -o(smallcase letter o) option to rename downloaded file from awscli-exe-linux-x86_64.zip to awscliv2.zip
$curl "https://awscli.amazonaws.com/awscli-exe-linux-x86_64.zip" -o "awscliv2.zip"
Step 2 : Unzip awscliv2.zip using unzip command
$ unzip awscliv2.zipStep 3: Install
$ sudo ./aws/install
optional switch
--install-dir - specific location other than default location which under current user.
--bin-dir - specific bin directory
--update - if you want update from version 1 to version 2
Update From AWS CLI version 1 to AWS CLI Version 2
$ which aws ~/.local/bin/awsStep 2 : Find installation directory of AWS CLI Version 1. result give --install-dir parameter value. Most cases bin directory and installation directory in version 1 same
$ ls ~/.local/bin/aws lrwxrwxrwx. 1 oracle oinstall 43 Apr 11 20:51 /home/oracle/.local/bin/awsStep 3 : use following command to upgrade from version 1 to version 2
sudo ./aws/install --bin-dir /usr/local/bin --install-dir /usr/local/aws-cli --update
Configure AWS CLI
1. Configure Credential - Use aws configure command to set aws access key id, aws secret access key, default region name and default output format.
[oracle@devBase aws]$ aws configure AWS Access Key ID [****************ksdk]: AWS Secret Access Key [****************klfk]: Default region name [ap-south-1]: Default output format [None]:
These information store under .aws directory of current user. This .aws directory have two file config and credentials. config file store region and output format while credentials store aws access key id and aws secret access key.
[oracle@devBase aws]$ ls ~/.aws/ config credentials [oracle@devBase aws]$ cat ~/.aws/config [default] region = ap-south-1 [oracle@devBase aws]$ cat ~/.aws/credentials [default] aws_access_key_id = jsdaflksdk aws_secret_access_key = kfsldafklfk
Here [default] indicate that this is default profile.
How to update region, output format, aws access key id, aws secret access key
Use set option to set these value
[oracle@devBase aws]$ aws configure set region ap-south-2 --profile default [oracle@devBase aws]$ aws configure get region --profile default ap-south-2Edit credential or config file
[oracle@devBase aws]$ vim ~/.aws/config
How to add multiple profile
1. Using aws cli - use --profile switch to add different profile.[oracle@devBase aws]$ aws configure --profile test AWS Access Key ID [None]: asdfkasdkjf AWS Secret Access Key [None]: akdfldsjakf Default region name [None]: us-west-1 Default output format [None]: tableyou can check the result
[oracle@devBase aws]$ cat ~/.aws/credentials [default] aws_access_key_id = jsdaflksdk aws_secret_access_key = kfsldafklfk [test] aws_access_key_id = asdfkasdkjf aws_secret_access_key = akdfldsjakf [oracle@devBase aws]$ cat ~/.aws/config [default] region = ap-south-2 [profile test] region = us-west-1 output = table2. Edit config and credential file to add different profile.
$ vim ~/.aws/config [default] region = ap-south-2 [profile test] region = us-west-1 output = table [profile test2] region = us-west-2 output = jsonTo use a named profile for multiple commands, you can avoid specifying the profile in every command by setting the AWS_PROFILE environment variable at the command line.
$ export AWS_PROFILE=test
Enable Command Completion
To enable command complettion, run the command for the shell that you're using. You can add the command to your shell's RC file to run it each time you open a new shell. In each command, replace the path /usr/local/aws/bin with the one found on your system in the previous section.[oracle@devBase aws]$ complete -C '~/.local/bin/aws_completer' aws
note : replace above red marked path to your system aws_completer location.Reference :
https://pip.pypa.io//en/latest/installing/#do-i-need-to-install-pip
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/how-to-install-python-3-and-set-up-a-local-programming-environment-on-centos-7
error
https://github.com/pypa/pip/issues/4186
https://github.com/jasperproject/jasper-client/issues/17
https://github.com/ethereum/viper/issues/276
https://github.com/retspen/webvirtcloud/issues/137
https://github.com/aws/aws-cli/issues/2654
https://github.com/aws/aws-cli/issues/1522
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/31512422/pip-install-r-oserror-errno-13-permission-denied/31512489
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)